Hair Loss Treatments in turkey
a combination of cutting-edge technology, experienced medical professionals, and competitive pricing. With a thriving medical tourism industry focused on hair restoration, Turkey attracts thousands of patients from around the world seeking effective solutions for hair loss.
Hair loss, whether due to genetics, hormonal imbalances, or other factors, can have a significant impact on an individual’s self-esteem and quality of life. Fortunately, advancements in hair transplant techniques, along with a comprehensive approach to treatment, have made Turkey a preferred destination for those looking to regain their confidence and restore a full head of hair.
In this article, we’ll explore the various hair loss treatments available in Turkey, highlighting the state-of-the-art procedures, experienced medical professionals, and the overall experience for international patients seeking hair restoration services in this vibrant country.
Introduction to Hair Loss
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur gradually over time or suddenly and can be caused by various factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors. Hair loss can affect both men and women and can have significant emotional and psychological effects on individuals. Understanding the underlying causes of hair loss and exploring available treatment options are essential steps in managing this condition effectively.
what is Hair Loss?
Hair loss, medically referred to as alopecia, encompasses a spectrum from mild thinning to complete baldness. While shedding 50 to 100 hairs daily is considered normal, exceeding this range warrants attention.
Hair loss presents in diverse patterns. Some individuals undergo gradual thinning on the scalp’s crown, typical in aging men and women. Others experience patchy hair loss or receding hairlines, often observed in men. Complete baldness, although uncommon, may arise from specific medical conditions or treatments.
Common Causes and Types of Hair Loss
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Also known as male or female pattern baldness, it’s the most common type of hair loss. It’s hereditary and typically results in a receding hairline and thinning on the crown for men, while women often experience overall thinning.
- Telogen Effluvium: This condition occurs when there’s a significant stressor on the body, such as childbirth, surgery, illness, or extreme weight loss. It leads to a sudden shedding of hair, but it’s usually temporary.
- Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune disorder causes the body’s immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to sudden hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp or other areas of the body.
- Traction Alopecia: Constant pulling on the hair, often due to hairstyles like tight ponytails, braids, or extensions, can damage hair follicles and lead to hair loss.
- Medication-induced Hair Loss: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, antidepressants, and blood thinners, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients like iron, protein, or vitamins can lead to hair loss.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations due to pregnancy, menopause, thyroid disorders, or hormonal imbalances can cause hair loss.
- Scalp Conditions: Conditions like dandruff, fungal infections, or psoriasis can lead to hair loss if left untreated.
Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment for hair loss.
Hair Loss in Men and Women
Hair loss is a prevalent issue affecting both men and women, with various factors influencing its onset and progression. While it is a natural part of aging for many, understanding the underlying causes and available treatments is essential for effective management.
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness
The Nature of Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness, medically known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common form of hair loss in men. It typically follows a distinct pattern characterized by a receding hairline and thinning hair on the crown. This condition is primarily influenced by hormones called androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics play a significant role in male pattern baldness. Individuals with a family history of the condition are at a higher risk. The process involves the gradual shrinking of hair follicles over time, resulting in the production of shorter, finer hair strands, until eventually, the follicles cease to produce hair altogether.
Onset and Progression
Male pattern baldness can begin as early as the teenage years and tends to progress with age. By the age of 50, more than 50% of men experience some degree of hair loss due to this condition. Understanding the onset and progression of male pattern baldness is crucial for early intervention and treatment.
Exploring Hair Loss in Women
Patterns of Female Hair Loss
Hair loss in women differs from that in men, often presenting as a more diffuse thinning across the scalp. Female pattern hair loss typically involves overall thinning, with the most significant hair loss occurring at the crown of the head. Unlike men, women rarely experience complete baldness but may notice a significant reduction in hair volume.
Menopause and Hair Loss
Menopause-related hormonal changes can contribute to hair loss in women. Decreased levels of estrogen and progesterone, coupled with an increase in androgens, can lead to slower hair growth and thinning. While menopause-related hair loss is common, it can have a significant impact on self-esteem and emotional well-being.
Other Contributing Factors
In addition to hormonal changes, other factors such as stress, diet, and certain medical conditions can contribute to hair loss in women. Understanding these underlying factors is essential for developing effective treatment strategies tailored to individual needs.
Diagnosing Hair Loss
Importance of Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis is essential for determining the most appropriate treatment approach for hair loss. The diagnostic process typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and may include additional tests such as blood work or scalp biopsies.
Diagnostic Procedures
Medical professionals use various diagnostic procedures to assess hair loss, including a detailed medical history to identify underlying health conditions or medications that may contribute to hair loss. Physical examination of the scalp helps determine the pattern and extent of hair loss, while additional tests such as the hair pull test or scalp biopsy may be conducted to further evaluate the condition.
Role of Medical Professionals
Dermatologists play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating hair loss. With their expertise in skin, hair, and nail disorders, dermatologists can accurately assess the type and cause of hair loss, create personalized treatment plans, and provide ongoing support and guidance throughout the treatment process.
Comprehensive Guide to Hair Loss Treatments
Hair loss treatments encompass a range of medical interventions, natural remedies, and surgical options tailored to individual needs. From FDA-approved medications to emerging therapies, understanding the available treatment options is essential for effectively managing hair loss.
Medical Interventions
FDA-approved medications such as minoxidil and finasteride are commonly prescribed to slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth in both men and women. These treatments work by targeting different aspects of the hair growth cycle and require ongoing use to maintain their effectiveness.
Natural Remedies and Alternative Treatments
In addition to conventional medications, many individuals explore natural remedies and alternative treatments for hair loss. While some may find success with herbal supplements, essential oils, or dietary changes, it’s essential to approach these treatments with caution and consult with a healthcare professional before trying them.
Surgical Options and Procedural Solutions
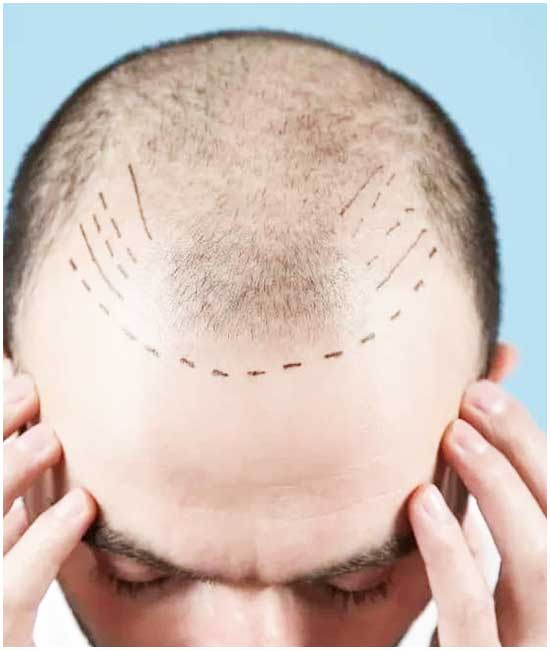
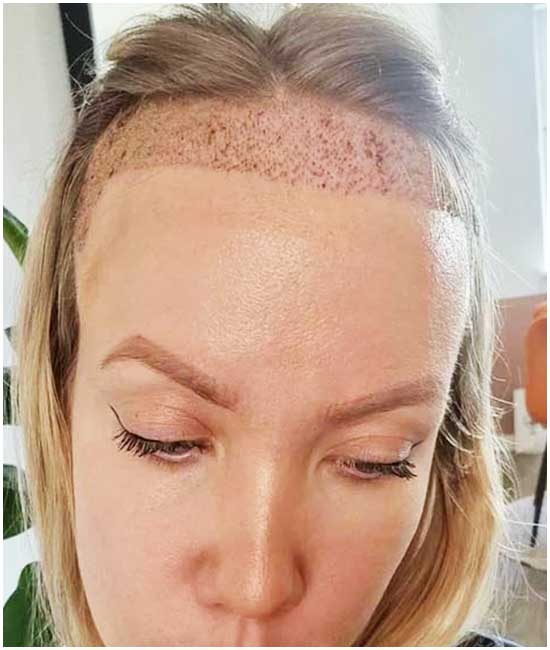
For individuals seeking more permanent solutions, surgical options such as hair transplant surgery offer effective solutions for hair restoration. Techniques such as Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) have evolved to provide natural-looking results with minimal downtime.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Ongoing research into hair loss has led to advancements in genetic therapies, stem cell treatments, and innovative surgical techniques. Staying informed about these emerging treatments is crucial for individuals seeking the latest options for hair loss management.
Special Focus: Hair Loss Treatment for Women
Hair loss treatment for women requires a tailored approach that addresses the unique hormonal and genetic factors influencing hair loss. From topical treatments to hormonal therapies, understanding the specific needs of women experiencing hair loss is essential for effective treatment.
Unique Aspects of Female Hair Loss
Hair loss in women often presents differently than in men, with overall thinning rather than specific patterns of baldness. Hormonal changes during menopause, along with other factors such as stress and nutritional deficiencies, contribute to hair loss in women.
Effective Treatments for Women
Treatment options for female hair loss include topical treatments, hormonal therapies, nutritional interventions, and hair transplant surgery. By addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances and other contributing factors, women can effectively manage hair loss and restore hair health.
Understanding and Managing Alopecia
Alopecia, a term for hair loss, encompasses various types with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. From androgenetic alopecia to alopecia areata, understanding these types of alopecia is essential for effective management and treatment.
Types of Alopecia
Alopecia presents in various forms, including androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, traction alopecia, and cicatricial alopecia. Each type has its own characteristics, causes, and treatment options.
Treatment Options
Treatment for alopecia varies depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Topical Treatments:
For mild cases, topical treatments can be effective, especially in alopecia areata. These treatments often contain ingredients that stimulate hair growth or prevent further thinning when applied directly to the scalp.
Corticosteroids:
Anti-inflammatory drugs like corticosteroids are commonly used to treat alopecia areata. They can be administered as injections, oral pills, or topical ointments, depending on the severity and extent of hair loss.
Immunotherapy:
In severe cases of alopecia areata, immunotherapy may be recommended. This treatment involves stimulating the body’s immune system to promote hair regrowth and prevent further hair loss.
Minoxidil (Rogaine):
Minoxidil is an over-the-counter medication commonly used to treat androgenetic alopecia. It is applied topically to the scalp and works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, promoting hair growth and preventing further loss.
Hair Transplant Surgery:
Hair transplant surgery is a surgical option for certain types of alopecia, such as androgenetic alopecia. During this procedure, hair follicles are transplanted from areas of the scalp with healthy hair growth to areas experiencing hair loss, resulting in natural-looking hair restoration.
Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medical treatments, making lifestyle modifications can help manage alopecia and promote overall hair health. These modifications may include:
- Dietary Changes: Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients like protein, iron, vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids can support hair growth and strength.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss, so practicing stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises may be beneficial.
- Avoiding Harsh Treatments: Minimizing the use of harsh chemicals, heat styling tools, and tight hairstyles can help prevent further damage to the hair follicles.
- Scalp Care: Gentle scalp massage and regular cleansing can promote blood circulation to the scalp and support hair growth.
By incorporating these lifestyle modifications along with appropriate medical treatments, individuals with alopecia can effectively manage their condition and maintain healthy hair growth.
Conclusion
Hair loss is a common concern for both men and women, influenced by a variety of factors including genetics, hormones, and lifestyle. Understanding the different types of hair loss, their causes, and available treatment options is essential for effective management and restoration of hair health. By consulting with medical professionals, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and exploring appropriate treatment modalities, individuals experiencing hair loss can regain confidence and achieve optimal hair growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is hair loss permanent?
Hair loss can be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying cause. While some forms of hair loss, such as alopecia areata, may resolve on their own or respond well to treatment, others, like androgenetic alopecia, may be progressive and require ongoing management.
2. Are there any natural remedies for hair loss?
Some natural remedies, such as essential oils, herbal supplements, and dietary changes, may help support hair health and growth. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies to ensure safety and effectiveness.
3. Can stress cause hair loss?
Yes, chronic stress can contribute to hair loss by disrupting the normal hair growth cycle. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and stress-reducing activities may help minimize hair loss associated with stress.
4. What role does genetics play in hair loss?
Genetics can significantly influence the risk of developing certain types of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia. Individuals with a family history of hair loss are more likely to experience similar patterns of hair loss themselves.
5. When should I see a doctor about hair loss?
If you’re experiencing significant or persistent hair loss, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or trichologist. They can evaluate your condition, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs.